Supervised learning techniques
- Feature selection Mutual information
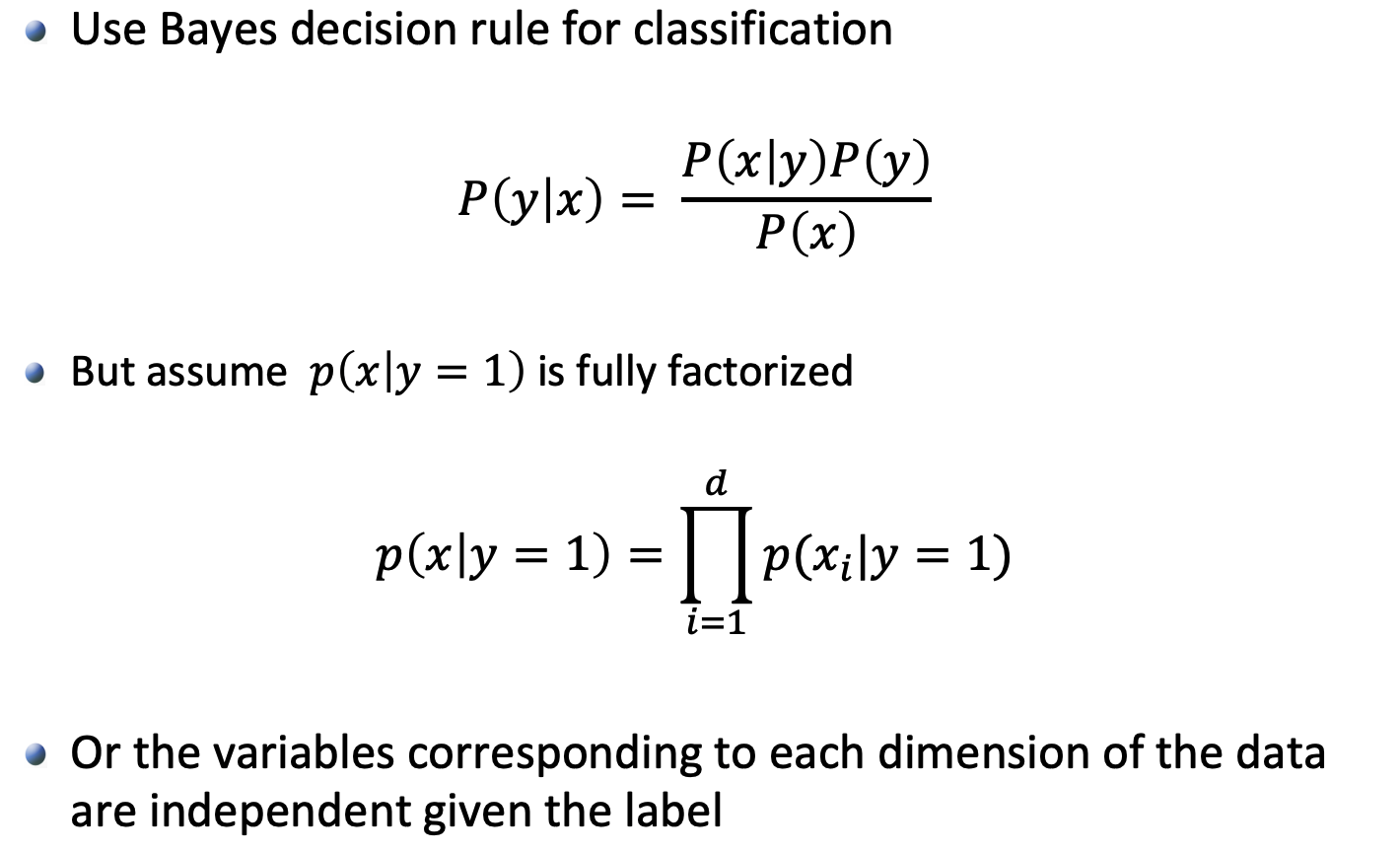
- Bayes decision rule Naïve Bayes
- Linear classifier Logistic regression Support vector machine
- Nonlinear classifier K-nearest neighbors
- Neural networks Single neuron ≈ logistic regression Deep neural networks
- Regression Linear regression Polynomial regression Ridge regression
1. Classifiers
1.1 Naive Bayes Classifier
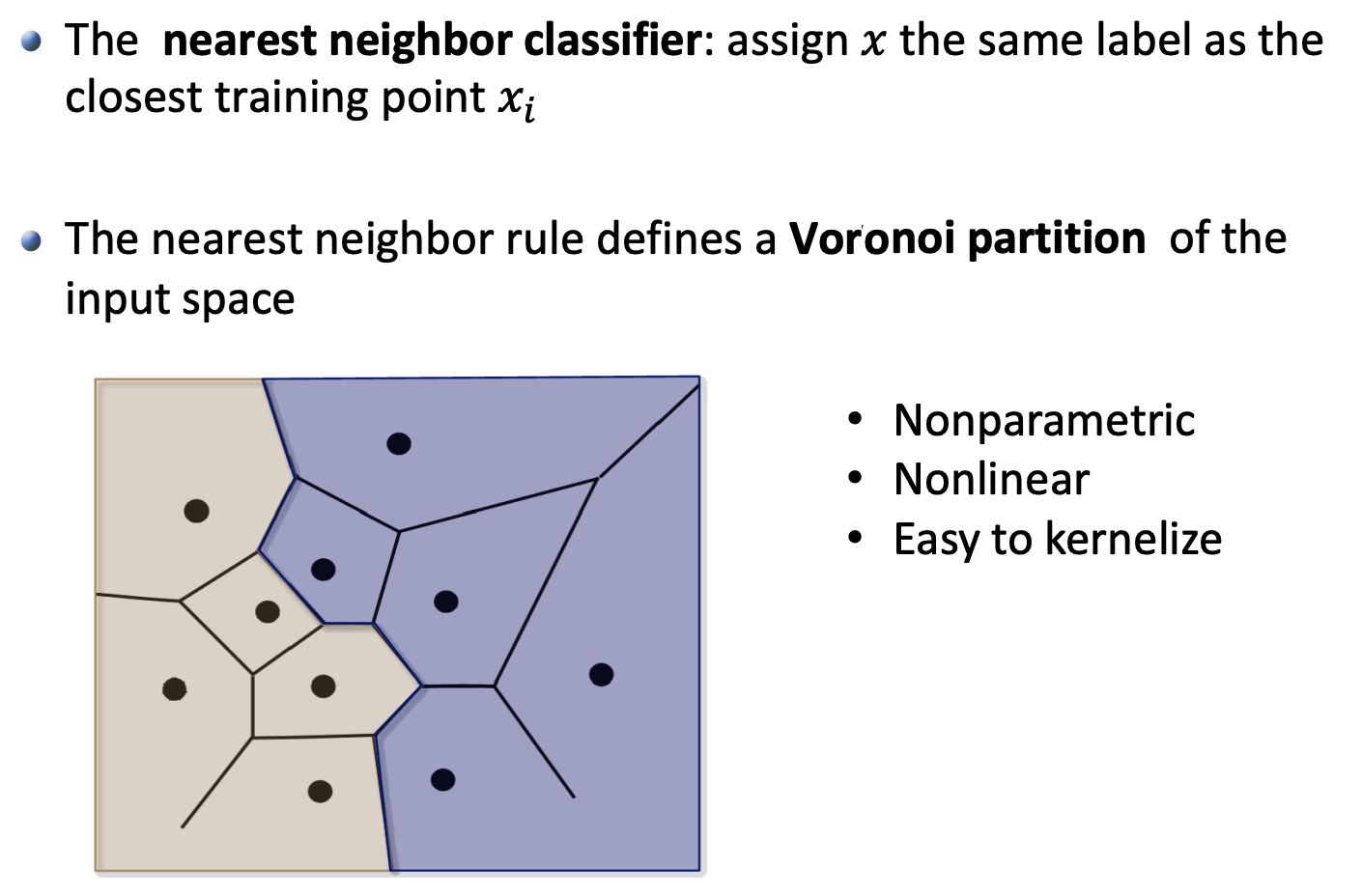
1.2 Nearest Neighbor Classifier (KNN)

1.3 Maximum Margin Classifier (SVM)
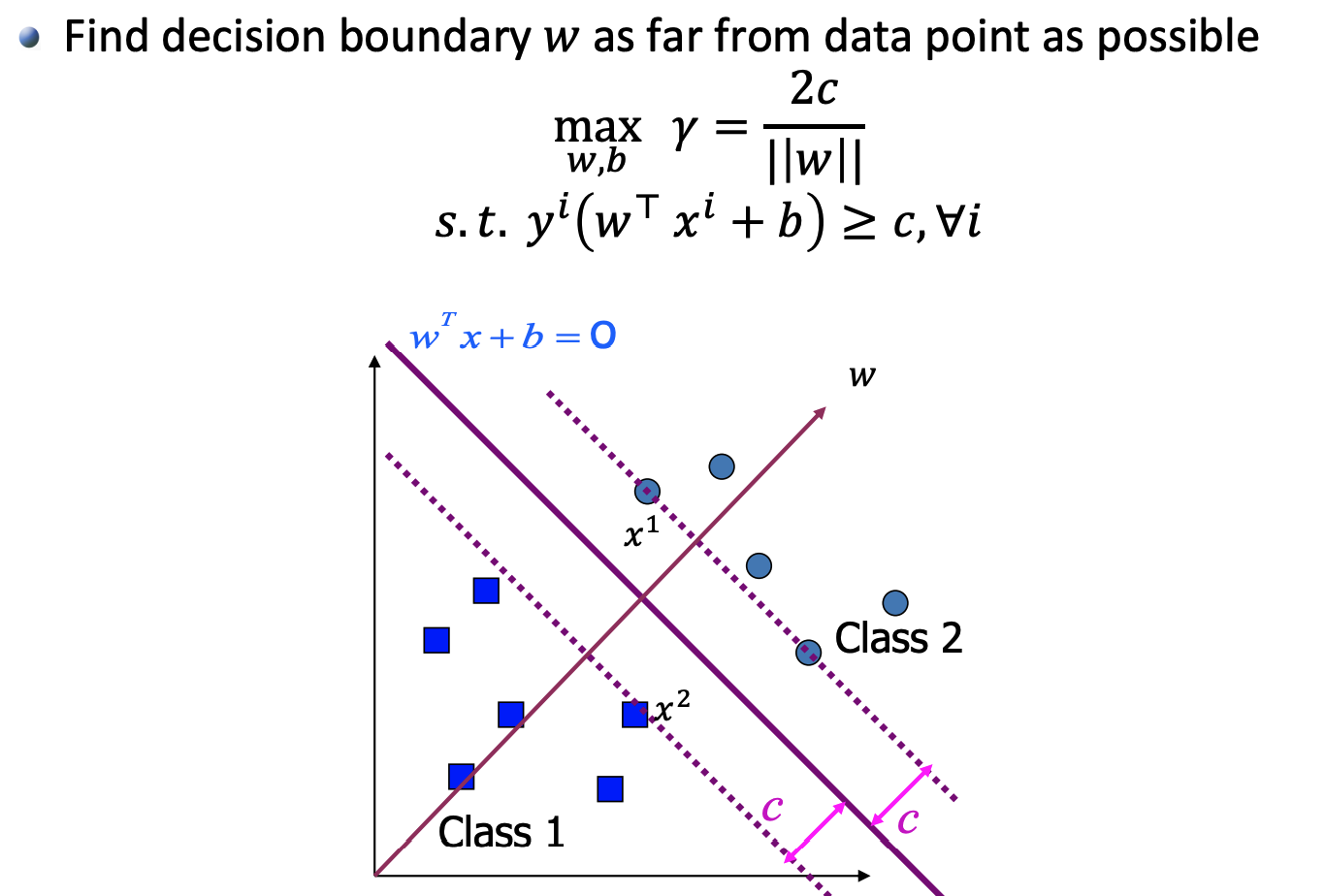
因为这里的 $c$ 为常数,因此可以除到 “$\ge$” 左侧的参数 $w,b$ 中,这样就得到了 Support Vector Machine(SVM) 的基本形式 \(\min_{w,b}\|w\|^2\)
\[s.t.\text{ }y^i(w^Tx^i+b)\ge 1,\forall i\]where $y^i=\pm 1$ 表示 $x^i$ 属于 Class 1 or Class 2
Support Vectors are the points on the lines $w^Tx+b=\pm 1$
1.3.1 Dual problem of SVM
Firstly convert SVM equation to standard form \(\min_{w,b}\frac{1}{2}w^Tw\)
\[s.t.\text{ }1-y^i(w^Tx^i+b)\le 0,\forall i\]Then construct Lagrangian function \(L(w,\alpha,\beta)=\frac{1}{2}w^Tw+\sum_{i=1}^m\alpha_i(1-y^i(w^Tx^i+b))\)
- when $1-y^i(w^Tx^i+b)=0,\alpha_i > 0$
- when $1-y^i(w^Tx^i+b)\ne 0,\alpha_i = 0$
Take derivative and set to zero (找最优的 $w^*$) \(\frac{\partial L}{\partial w}=0\to w=\sum_{i=1}^m\alpha_iy^ix^i\)
\[\frac{\partial L}{\partial b}=0\to \sum_{i=1}^m\alpha_iy^i=0\]Plug back into Lagrangian and simplify to get the dual problem of SVM: \(L(w,\alpha,\beta)=\sum_{i=1}^m\alpha_i-\frac{1}{2}\sum_{i,j=1}^m\alpha_i\alpha_jy^iy^j({x^i}^Tx^j)\)
\[s.t.\begin{cases} \alpha_i\ge 0 \text{ }\forall i\\ \sum_i^m\alpha_iy^i=0 \end{cases}\]通过求解以上 quadratic programming,求得 $\alpha_i^*,y^i$
1.3.2 Solve dual problem
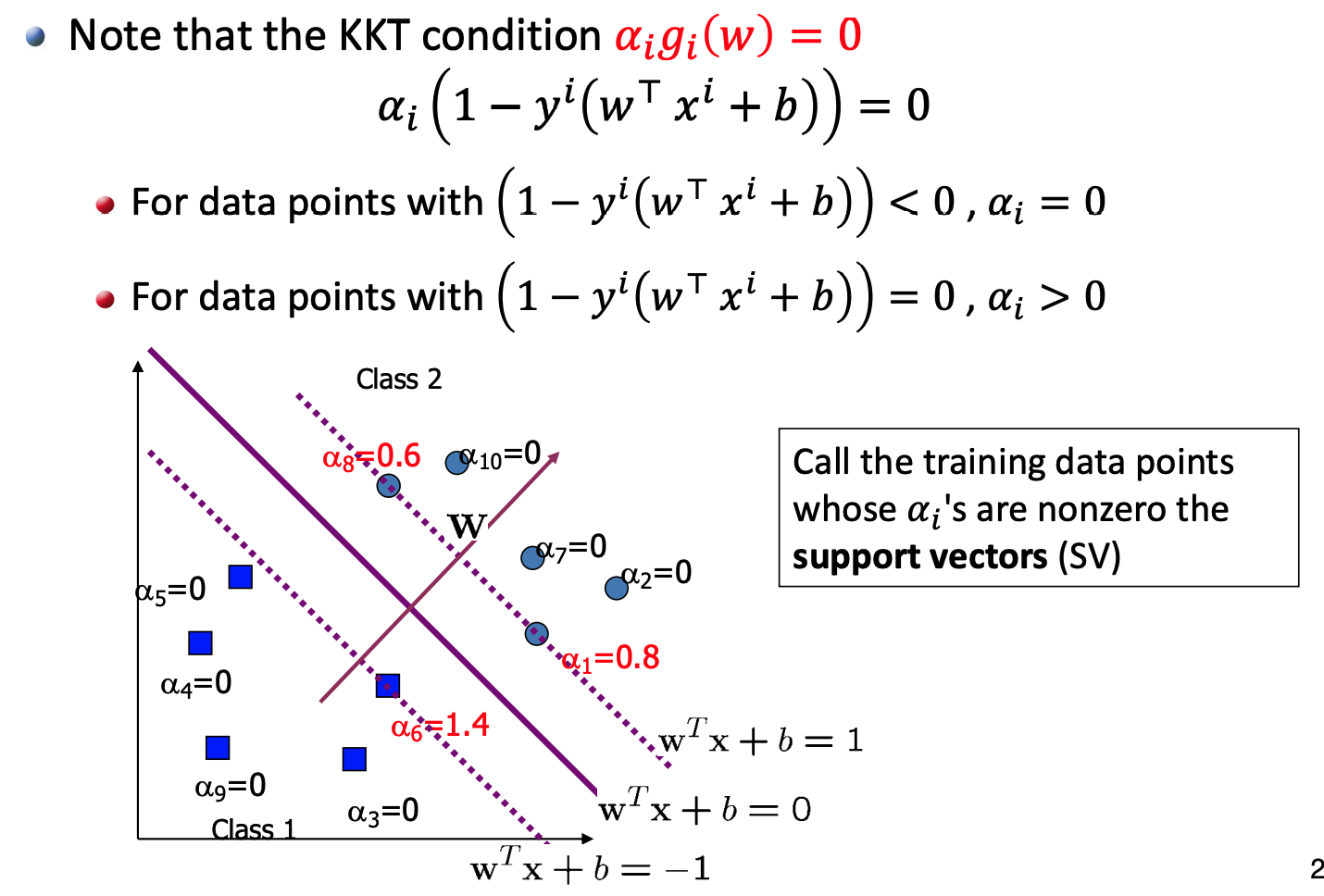
首先求出 $w$: \(w=\sum_{i=1}^m\alpha_iy^ix^i\)
在对于任意 data $i$ such that $\alpha_i>0$,求出 $b$: \(1-y^i(w^Tx^i+b)=0\)
2. Regression
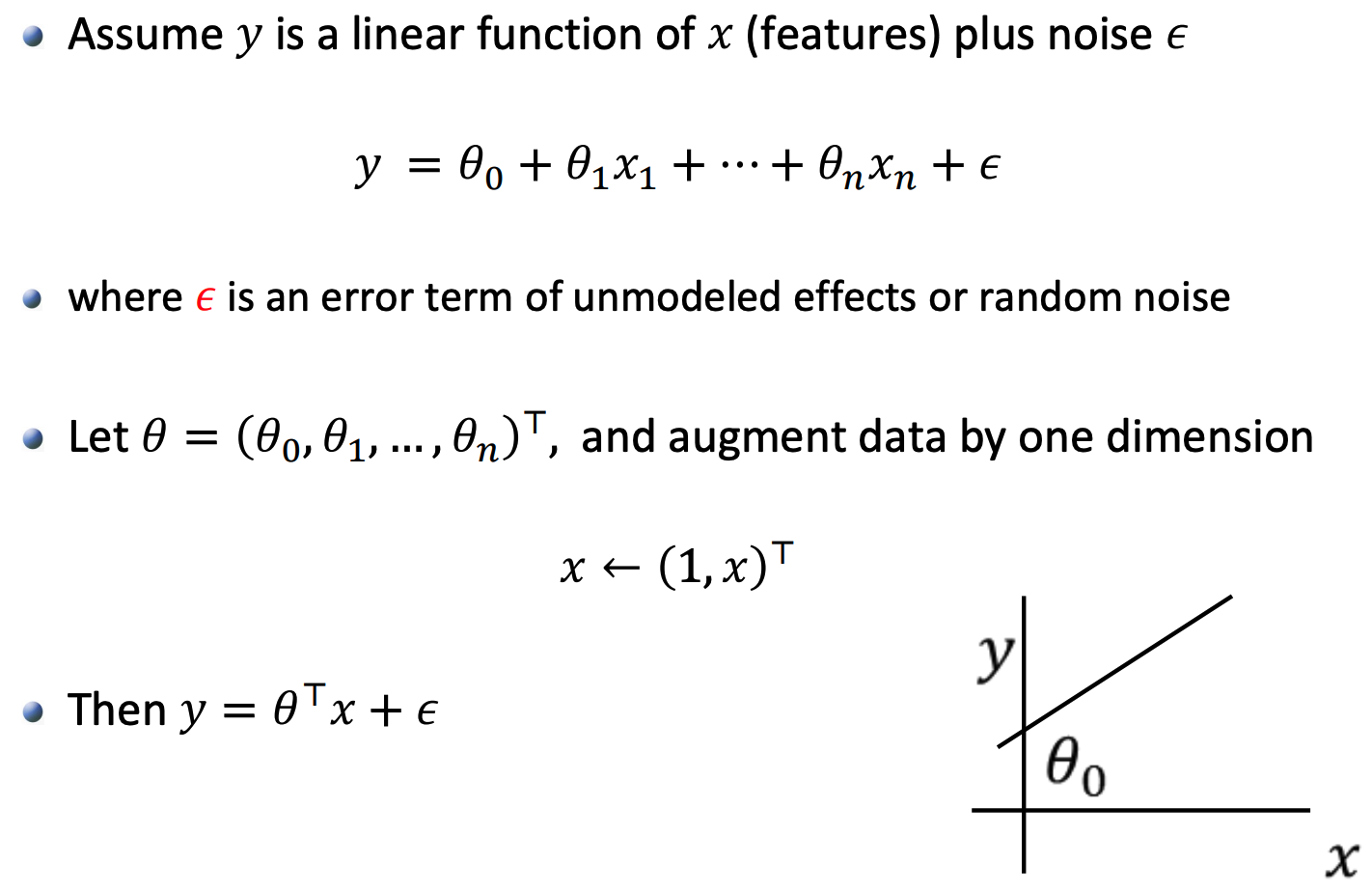
2.1 Linear Regression Model
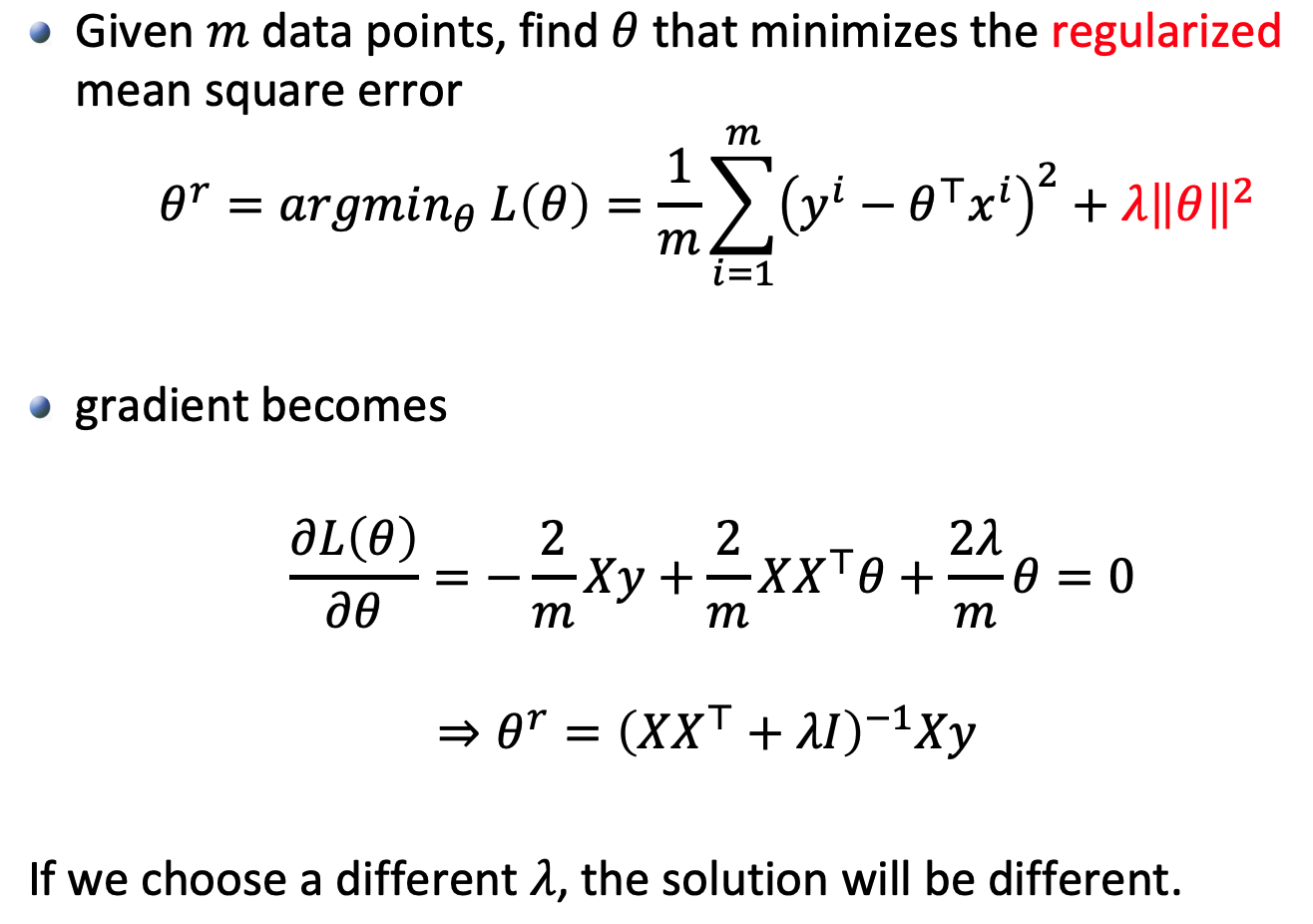
2.2 Ridge Regression
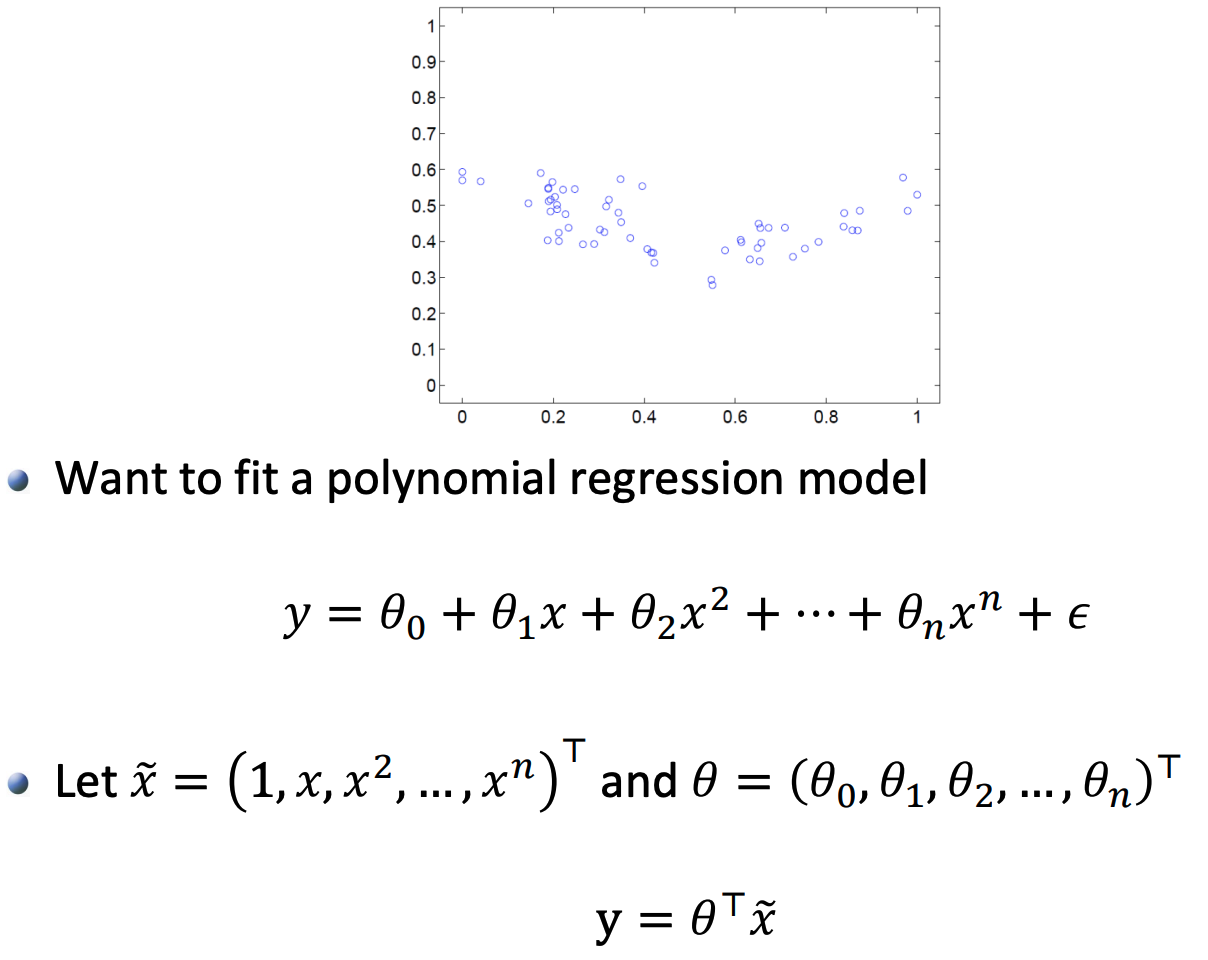
2.3 Nonlinear Regression
Document Information
- Author: Zeka Lee
- Link: https://zhekaili.github.io/0004/07/01/supervised-Classifiers-and-Regression/
- Copyright: 自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)